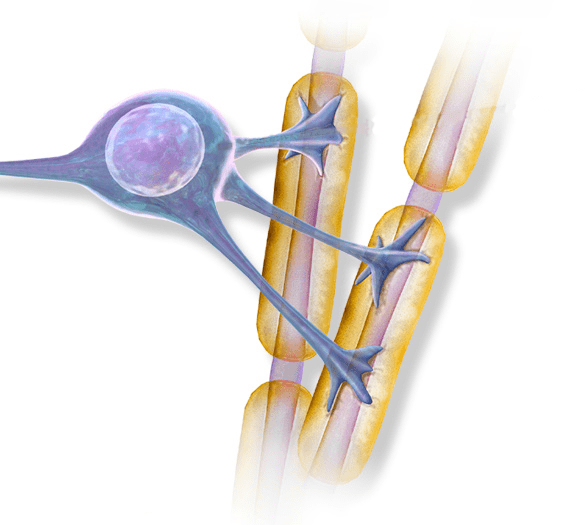
- Age-dependent regulation of axoglial interactions and behavior by oligodendrocyte AnkyrinGby Xiaoyun Ding on April 15, 2024 at 10:00 am
The bipolar disorder (BD) risk gene ANK3 encodes the scaffolding protein AnkyrinG (AnkG). In neurons, AnkG regulates polarity and ion channel clustering at axon initial segments and nodes of Ranvier. Disruption of neuronal AnkG causes BD-like phenotypes in mice. During development, AnkG is also expressed at comparable levels in oligodendrocytes and facilitates the efficient assembly of paranodal junctions. However, the physiological roles of glial AnkG in the mature nervous system, and its…
- Navigating the Uncharted Territory of Pediatric-Onset Multiple Sclerosis in a 12-Year-Old Male: A Case Studyby Han Grezenko on April 15, 2024 at 10:00 am
This case report presents an atypical instance of pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis (MS) in a 12-year-old male, a demographic less commonly affected by this condition. The patient’s clinical course was marked by severe and progressive symptoms, including lower limb weakness and loss of bowel/bladder control, diverging from the typical relapsing-remitting pattern observed in pediatric MS. Despite initial resistance to high-dose steroid treatment, his condition was ultimately stabilized through…
- A Comparative Review of Typical and Atypical Optic Neuritis: Advancements in Treatments, Diagnostics, and Prognosisby Noah J Spillers on April 15, 2024 at 10:00 am
Optic neuritis (ON) is a debilitating condition that through various mechanisms, including inflammation or demyelination of the optic nerve, can result in partial or total permanent vision loss if left untreated. Accurate diagnosis and promptly initiated treatment are imperative related to the potential of permanent loss of vision if left untreated, which can lead to a significant reduction in the quality of life in affected patients. ON is subtyped as “typical” or “atypical” based on underlying…
- Oligodendrocytes: Myelination, Plasticity, and Axonal Supportby Mikael Simons on April 15, 2024 at 10:00 am
The myelination of axons has evolved to enable fast and efficient transduction of electrical signals in the vertebrate nervous system. Acting as an electric insulator, the myelin sheath is a multilamellar membrane structure around axonal segments generated by the spiral wrapping and subsequent compaction of oligodendroglial plasma membranes. These oligodendrocytes are metabolically active and remain functionally connected to the subjacent axon via cytoplasmic-rich myelinic channels for movement…
- Isolation and Culture of Mouse Primary Microglia and Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cellsby Zihao Li on April 15, 2024 at 10:00 am
Microglia and oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) are critical glia subsets in the central nervous system (CNS) and are actively engaged in a body of diseases, such as stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, etc. Microglia and OPC serve as compelling tools for the study of CNS diseases as well as the repair and damage of myelin sheath in vitro. In this protocol, we summarized a method which is capable of using the same batch of new-born mice to isolate and culture microglia and OPCs….
- Morphological correlates of pyramidal cell axonal myelination in mouse and human neocortexby Maria Pascual-García on April 13, 2024 at 10:00 am
The axons of neocortical pyramidal neurons are frequently myelinated. Heterogeneity in the topography of axonal myelination in the cerebral cortex has been attributed to a combination of electrophysiological activity, axonal morphology, and neuronal-glial interactions. Previously, we showed that axonal segment length and caliber are critical local determinants of fast-spiking interneuron myelination. However, the factors that determine the myelination of individual axonal segments along…
- Interaction between Oligodendrocytes and Interneurons in Brain Development and Related Neuropsychiatric Disordersby Yingqi Liu on April 13, 2024 at 10:00 am
A variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders have recently been shown to be highly associated with the abnormal development and function of oligodendrocytes (OLs) and interneurons. OLs are the myelin-forming cells in the central nervous system (CNS), while interneurons are important neural types gating the function of excitatory neurons. These two types of cells are of great significance for the establishment and function of neural circuits, and they share similar developmental origins…
- Adult Neurogenesis of Teleost Fish Determines High Neuronal Plasticity and Regenerationby Evgeniya Vladislavovna Pushchina on April 13, 2024 at 10:00 am
Studying the properties of neural stem progenitor cells (NSPCs) in a fish model will provide new information about the organization of neurogenic niches containing embryonic and adult neural stem cells, reflecting their development, origin cell lines and proliferative dynamics. Currently, the molecular signatures of these populations in homeostasis and repair in the vertebrate forebrain are being intensively studied. Outside the telencephalon, the regenerative plasticity of NSPCs and their…
- Comprehensive Analysis of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Brain Metastasis through Integrated Single-Cell Transcriptomicsby Vanessa G P Souza on April 13, 2024 at 10:00 am
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a highly prevalent and lethal form of lung cancer, comprising approximately half of all cases. It is often diagnosed at advanced stages with brain metastasis (BM), resulting in high mortality rates. Current BM management involves complex interventions and conventional therapies that offer limited survival benefits with neurotoxic side effects. The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a complex system where cancer cells interact with various elements, significantly…
- Transcription factor Olig2 is a major downstream effector of histone demethylase Phf8 during oligodendroglial developmentby Marco Kremp on April 13, 2024 at 10:00 am
The plant homeodomain finger protein Phf8 is a histone demethylase implicated by mutation in mice and humans in neural crest defects and neurodevelopmental disturbances. Considering its widespread expression in cell types of the central nervous system, we set out to determine the role of Phf8 in oligodendroglial cells to clarify whether oligodendroglial defects are a possible contributing factor to Phf8-dependent neurodevelopmental disorders. Using loss- and gain-of-function approaches in…
- Functional myelin in cognition and neurodevelopmental disordersby Hasni Khelfaoui on April 13, 2024 at 10:00 am
In vertebrates, oligodendrocytes (OLs) are glial cells of the central nervous system (CNS) responsible for the formation of the myelin sheath that surrounds the axons of neurons. The myelin sheath plays a crucial role in the transmission of neuronal information by promoting the rapid saltatory conduction of action potentials and providing neurons with structural and metabolic support. Saltatory conduction, first described in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), is now generally recognized as a…
- Early life phenobarbital exposure dysregulates the hippocampal transcriptomeby Seán Quinlan on April 12, 2024 at 10:00 am
Introduction: Phenobarbital (PB) and levetiracetam (LEV) are the first-line therapies for neonates with diagnosed seizures, however, a growing body of evidence shows that these drugs given during critical developmental windows trigger lasting molecular changes in the brain. While the targets and mechanism of action of these drugs are well understood-what is not known is how these drugs alter the transcriptomic landscape, and therefore molecular profile/gene expression during these critical…
- Human Glial Cells as Innovative Targets for the Therapy of Central Nervous System Pathologiesby Giulia Magni on April 12, 2024 at 10:00 am
In vitro and preclinical in vivo research in the last 35 years has clearly highlighted the crucial physiopathological role of glial cells, namely astrocytes/microglia/oligodendrocytes and satellite glial cells/Schwann cells in the central and peripheral nervous system, respectively. Several possible pharmacological targets to various neurodegenerative disorders and painful conditions have therefore been successfully identified, including receptors and enzymes, and mediators of neuroinflammation….
- Neddylation orchestrates the complex transcriptional and posttranscriptional program that drives Schwann cell myelinationby Paula Ayuso-García on April 12, 2024 at 10:00 am
Myelination is essential for neuronal function and health. In peripheral nerves, >100 causative mutations have been identified that cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder that can affect myelin sheaths. Among these, a number of mutations are related to essential targets of the posttranslational modification neddylation, although how these lead to myelin defects is unclear. Here, we demonstrate that inhibiting neddylation leads to a notable absence of peripheral myelin and axonal loss both…
- Improving the sensitivity of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-antibody testing: exclusive or predominant MOG-IgG3 seropositivity-a potential diagnostic pitfall in patients with MOG-EM/MOGADby S Jarius on April 12, 2024 at 10:00 am
CONCLUSIONS: In some patients with MOG-EM/MOGAD, MOG-IgG is either exclusively or predominantly MOG-IgG3. Thus, the use of IgG1-specific assays might only partly overcome the current limitations of MOG-IgG testing and-just like H+L- and Fcγ-specific testing-might overlook some genuinely seropositive patients. This would have potentially significant consequences for the management of patients with MOG-EM/MOGAD. Given that IgG3 chiefly detects proteins and is a strong activator of complement and…